Overview
The University of Massachusetts (UMass) Amherst is a member of the Massachusetts public higher education system, which consists of 15 community colleges, nine state universities, and five UMass campuses. In 1964, UMass Amherst became one of the five public institutions of higher learning in the UMass system, in accordance with Chapter 75 of the Massachusetts General Laws. UMass is led by a president who oversees the UMass system and by a chancellor at each UMass campus. It is also governed by a board of trustees composed of 22 members, with 17 members who are appointed by the Governor for five-year terms and 5 UMass students who are elected by the student body for one-year terms. The board shapes general policies that govern all five UMass campuses. The chancellor of UMass Amherst, as the administrative head of the campus, reports to the president and is supported by vice chancellors, a provost, and the director of athletics.
As of fall 2023, UMass Amherst had a total enrollment of 31,810 students (23,936 undergraduate and 7,874 graduate students) and approximately 9,373 employees (6,135 full-time and 3,238 part-time employees). According to Section 7 of Chapter 75 of the General Laws, “The [UMass system] trustees shall prepare and submit a detailed budget in such form and manner as the governor, secretary and general court may direct.” UMass Amherst had an operating budget of $1,547,122,000 for the 2023 fiscal year and $1,458,822,000 for the 2022 fiscal year. UMass Amherst had state appropriations of $421,771,000 and $448,412,000 for fiscal years 2022 and 2023, respectively.
Website Accessibility
Americans with Disabilities Act
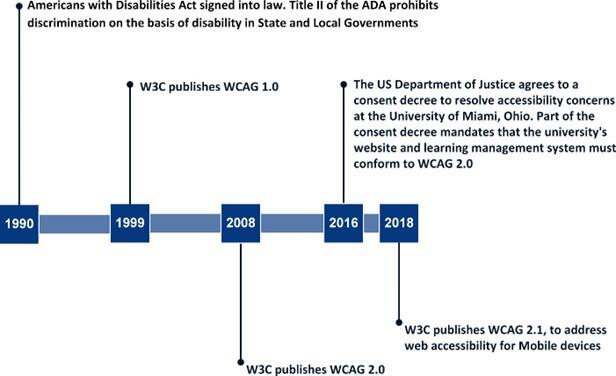
In 1990, the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), a comprehensive civil rights law prohibiting discrimination based on disability, came into effect. Title II of the ADA covers state-funded programs such as universities, community colleges, and career and technical education programs, including all activities of state and local governments, regardless of whether these entities receive federal financial assistance. (See 42 US Code § 12131B65). More recently, the Justice Department filed a proposed consent decree to resolve allegations that Miami University in Oxford, Ohio, violated the ADA by using inaccessible classroom technologies and other technologies. As part of the consent decree, Miami University had to ensure that its web content and learning management systems conform with Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.0 AA standards. Additionally, the university was required to meet with every student who has a disability in order to develop an accessibility plan and procure web technology or software that best meets various accessibility standards.
WCAG
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), an international organization that oversees internet standards, released WCAG 1.0 in 1999. These guidelines aimed to offer directions on enhancing the accessibility of web content for people with disabilities. In 2008, W3C published WCAG 2.0. In 2018, W3C published WCAG 2.1, which was built on WCAG 2.0 to improve web accessibility on mobile devices and to further improve web accessibility for people with visual impairments and cognitive disabilities.
Progression of Internet Accessibility Standards
How People with Disabilities Use the Web
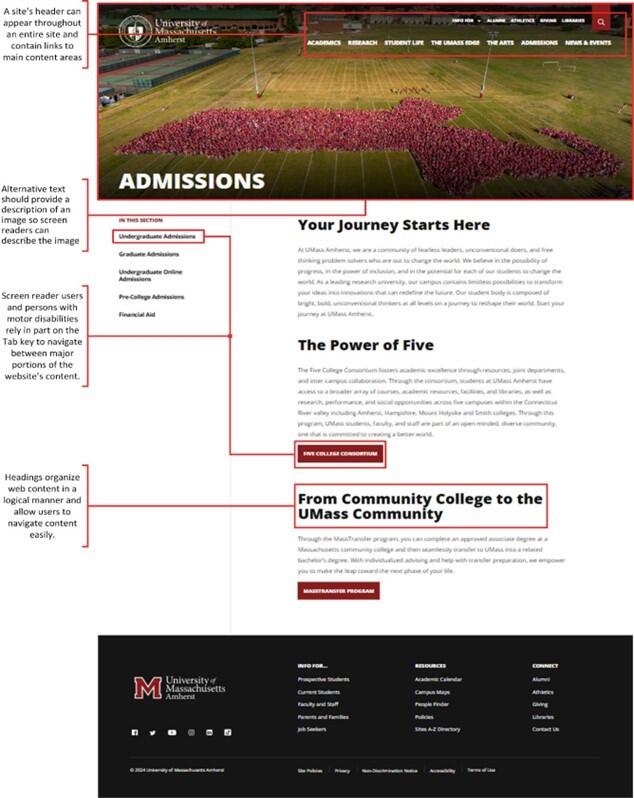
According to W3C, people with disabilities use assistive technologies and adaptive strategies specific to their needs to navigate web content. Examples of assistive technologies include screen readers, which read webpages aloud for people who cannot read text; screen magnifiers for individuals with low vision; and voice recognition software for people who cannot (or do not) use a keyboard or mouse. Adaptive strategies refer to techniques that people with disabilities employ to enhance their web interaction.3 These strategies might involve increasing text size, adjusting mouse speed, or enabling captions. To make web content accessible to people with disabilities, developers must ensure that various components of web development and interaction work together. This includes text, images, and structural code; users’ browsers and media players; and various assistive technologies.
UMass Amherst made efforts to create and maintain an accessible website in the following ways. Currently at the university, the Assistive Technology Center team performs accessibility reviews of webpages before they are published. Additionally, the university uses third-party software (called SiteImprove) to run weekly scans of the umass.edu website to identify accessibility issues.
Common Accessibility Features of a Website*
* This webpage was modified to fit in our report.
Blackboard LMS
According to UMass, Blackboard Learn Original is the third-party vendor learning management system (LMS)4 chosen by the university to help instructors provide effective and engaging learning in the classroom. The LMS allows instructors to conduct their courses either partly or entirely online and allows students to undertake a variety of actions, including taking tests, submitting homework assignments, watching lecture videos, keeping track of their grades, and engaging in student discussions. Blackboard’s website indicates that its products are generally designed and developed in alignment with WCAG 2.1 Level AA success criteria.
In spring 2023, UMass Amherst announced that it had selected a new LMS called Canvas. We did not test Canvas because it was not fully implemented by the university during the audit period. The university made this transition to address accessibility concerns, increase inclusivity for mobile users, and further integrate the learning and teaching experience.
Cybersecurity Awareness Training
Starting in 2008, in reaction to significant data losses faced by organizations in the US defense sector, the Center for Internet Security (CIS) introduced best practice guidelines for computer security known as CIS Controls. There are 18 controls; they are a set of prioritized cybersecurity actions that organizations can implement to protect against the most common cyber threats. CIS Control 14 (Security Awareness and Skills Training) focuses on the importance of developing and sustaining a security awareness program aimed at shaping employee behavior to be more security minded and adequately trained, thereby minimizing cybersecurity risks to the organization.
In the 2010s, the transition to cloud computing led to an increased focus on cloud security. At the same time, the rise of increased cyber threats highlighted the necessity for cooperative strategies to combat emerging digital challenges. As a result of various data breaches and other cyberattacks, there was an effort to invest in cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive information across organizations. The absence of cybersecurity training poses one of the highest risks an organization can face, as untrained employees are often the weakest link in its security defenses. Recognizing this, organizations have prioritized investments in cybersecurity training to educate their workforce about potential cyber threats, such as phishing scams and malware.
In 2010, the UMass board of trustees passed a new Information Security Policy (Doc. T10-089), which commits the university to adopt controls modeled on ISO 27002.5 This includes controls requiring employees to receive cybersecurity awareness training. According to the university’s President’s Office, in the intervening years, the university adopted CIS Controls, which require the university’s campuses to maintain a cybersecurity awareness training program across its entire workforce.
Currently, UMass Amherst has not updated its policies to require all of its employees to complete cybersecurity awareness training, and it does not enroll all of its employees in cybersecurity awareness training, although it is made available to employees who request it. There are no procedures or enforcement mechanisms in place to ensure cybersecurity training completion across UMass Amherst’s workforce. Depending on their work functions, certain employees in departments where Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act, and/or Payment Card Industry training is required receive different training programs that also include cybersecurity awareness training.
| Date published: | December 30, 2024 |
|---|