Core elements
Delivering effective treatment is a complex task. Treating addictive behavior involves many different components and must account for the multiple and diverse needs of individual patients. However, there are core activities that are fundamental components of comprehensive addiction treatment. [Source: Leshner, 1999]
Non-specific treatment effects
In the search for the most effective and specific treatment practices, it is essential to remember that non-specific or common factors account for a considerable amount of treatment outcome. Non-specific factors include: (1) the extra-therapeutic attributes that clients bring with them to treatment (e.g., education, family support); (2) relationship factors displayed by the treatment provider (e.g., empathy, caring, warmth); and (3) the hope, expectancies and placebo effects that often associate with the start of treatment. Clinicians should cultivate their non-specific treatment skills. Integrating non-specific treatment skills with gambling-specific treatment strategies holds the potential to maximize treatment benefits. [Source: Hubble, Duncan, & Miller, 1999]
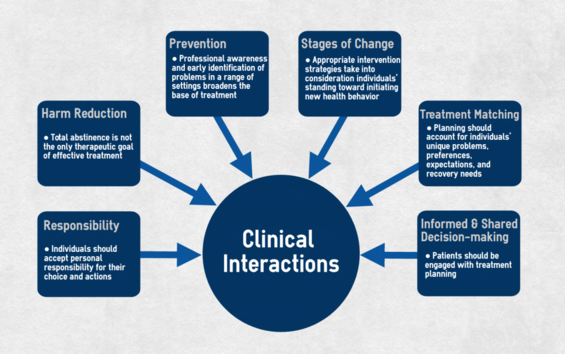
Guiding principles for clinical interactions
Treatment emergencies
It is difficult to establish a causal link between suicidal thoughts and behaviors and gambling-related problems. However, a number of studies have reported high rates of these issues among people with gambling-related problems. As with treating any disorder that might be associated with suicidal activity, it is important to remain vigilant. Threats of suicide can arise when losses lead to intense feelings of hopelessness, desperation, and conflict or when other conditions such as substance abuse, depression, or major mental illness coexist.
Clinicians who suspect that a client might be experiencing suicidal thoughts or planning should complete an urgent evaluation, followed by prompt treatment or referral, if required.
Discredited therapies
These guidelines show that evidence-based practice for gambling-related problems is an achievable goal. Unfortunately, the mental health treatment world includes many treatment approaches of questionable origins and efficacy. From crystals, to past lives, to aromatherapy, to facilitated communication – with an evidence-based perspective, it is easy to avoid such discredited treatments. In fact, some have suggested that it might be easier to know what doesn’t work than it is to rigorously determine what does work. [Source:Norcross, Koocher, & Garofalo, 2006, p. 515]
Sticking with evidence-based practices helps health providers avoid unintended consequences and chasing temporary improvements that only are the result of short-term placebo effects. Delphi Panel Experts’ Top Rating of Discredited Treatments for Mental/Behavioral Disorders provides an excellent resource ineffective problem gambling treatment methods.
Special populations
Evidence-based Guidelines make it easy to assume that all treatments are equally efficacious for all types of people. However, research in other areas suggests that it might be important to pick treatment approaches with consideration for individuating factors.
Among the many special populations that providers should account for are youth, older adults, women, Aboriginal/First Nation/Indian People, Ethno cultural minorities, the homeless, and those with psychiatric comorbidity. As the EBP Trinity illustrates, careful treatment planning that takes into account individuals’ unique backgrounds and circumstances is important to obtaining agreed upon treatment goals.
Contact
Phone
OPGS provides a range of programs and services across the continuum of care. If you or a loved one need immediate assistance regarding problem gambling, please call the Massachusetts Problem Gambling Helpline or visit https://gamblinghelplinema.org/
We can all help prevent suicide. The Lifeline provides 24/7, free and confidential support for people in distress, prevention and crisis resources for you or your loved ones, and best practices for professionals.
24./7. Info & referral for substance abuse services including crisis intervention and referrals for inpatient/outpatient treatment and where to go if uninsured.
Trained advocates are available to take your calls through our toll free, 24/7 hotline.
24/7. Support and referrals for parents with children of any age, as well as for other family members, care givers, friends and relatives.