Overview
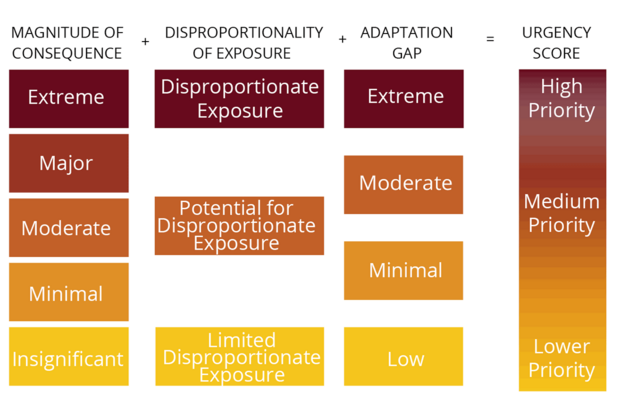
This Climate Assessment considers impacts across five sectors which represent major categories of projected impacts of climate change with common groupings of exposed assets, individuals, or resources, and that generally fall under the responsibility of similar state agencies. The primary objective of the Climate Assessment is to identify urgent climate risk statewide, as well as by each region and sector. Risk rankings were developed through discussions with the project working group and stakeholders, and considered:
-
How big of a climate effect will this have? Quantitative and qualitative indicators of the scale of potential impact, analyzed under the defined future climate scenario.
-
Will populations living in environmental justice areas be disproportionately affected? Demographic analysis of the distribution of impact across populations, particularly the Commonwealth’s identified environmental justice and socially vulnerable groups.
-
Are we currently doing enough to adapt to this impact? Assessment of current and planned adaptation plans and actions, and the potential benefits of additional adaptation action.
Sectors are a helpful organizational structure and allow for the prioritization across impacts with similar types of effects. However, it is important to note that the effects of climate change do not fall neatly within the defined sectors, and there are many interactions between impacts both within and across sectors. To the extent possible, these interactions are noted in the Climate Assessment in order to help draw these connections that may not be seen in the quantitative sectoral analysis.
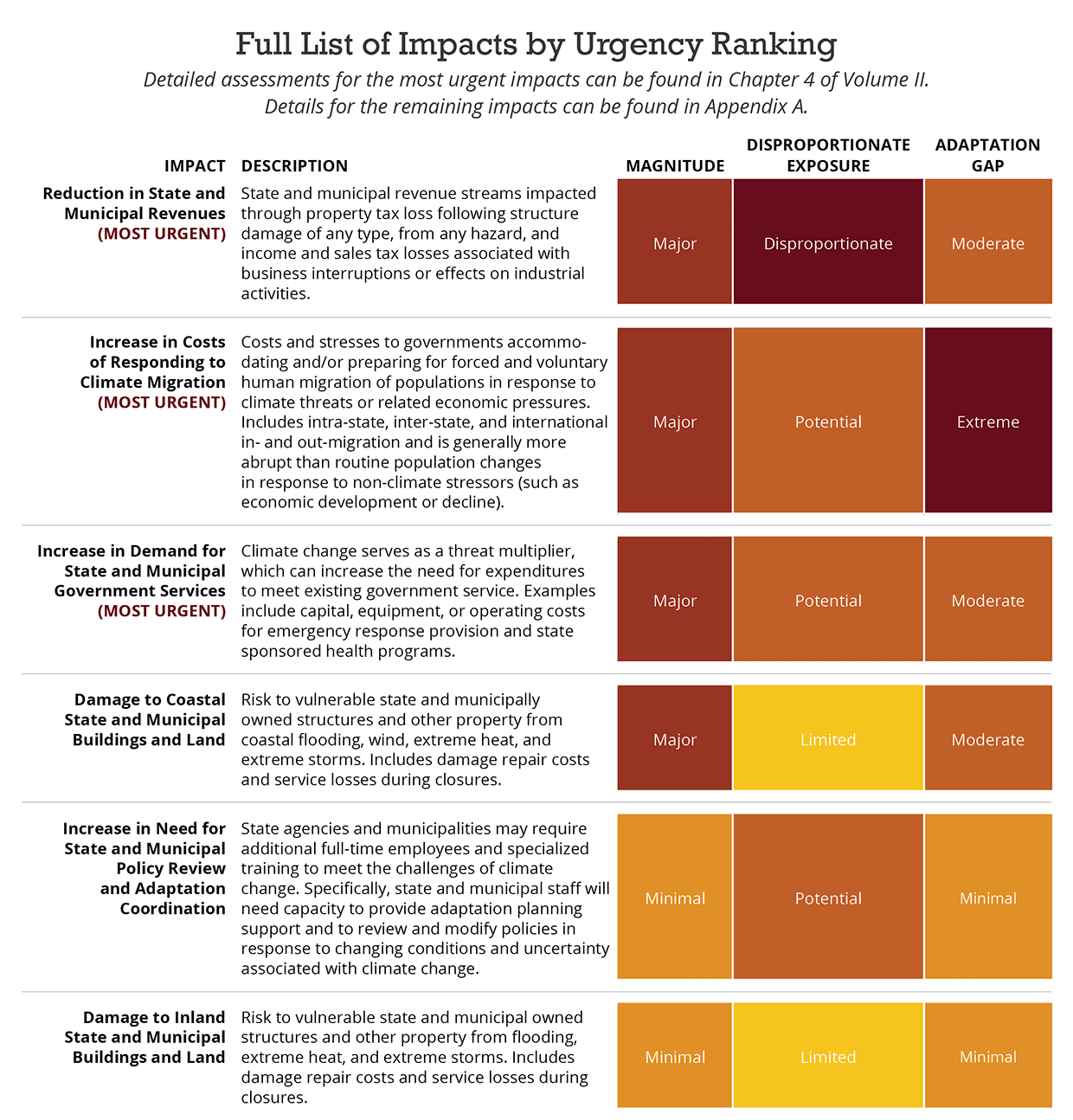
Full List of Impacts in the Governance Sector
Nine impacts were evaluated within the Governance Sector. Detailed assessments for the most urgent impacts can be found below and in Chapter 4 of Volume II. Details for the remaining impacts can be found in Appendix A.
Most Urgent Impact: Reduction in State and Municipal Revenues
State and municipal revenue streams impacted through property tax loss following structure damage of any type, from any hazard, and income and sales tax losses associated with business interruptions or effects on industrial activities.
Major Level of Consequence
Massachusetts municipalities could experience $104 million in lost revenues from a 3 ft sea level rise (1.4 percent of current property taxes in 89 coastal municipalities).
Disproportionate Exposure
Lost property tax value from coastal structures is the largest category of expected impact, and could disproportionally impact municipalities with higher proportions of population in EJ block groups.
Moderate Adaptation Gap
Adaptation actions focused on reducing property damage (particularly from coastal flooding) will help to mitigate this impact.
Most Urgent Impact: Increase in Costs of Responding to Climate Migration
Costs and stresses to governments accommodating and/or preparing for forced and voluntary human migration of populations in response to climate threats or related economic pressures. Includes intra-state, inter-state, and international in- and out-migration, and is generally more abrupt than routine population changes in response to non-climate stressors (such as economic development or decline).
Major Level of Consequence
Global and national concern for climate migration is appropriately high, and while the impact for Massachusetts is uncertain, several studies suggest Massachusetts could be a “receiving zone” because of its more northerly location in the U.S. and less extreme summer climate than other locations.
Potential for Disproportionality
Unable to estimate – current experience suggests areas with current concentrations of ethnic groups may be receiving areas for climate migration.
Extreme Adaptation Gap
daptation action to prepare communities for a possible influx of climate migrants is very limited, to date.
Most Urgent Impact: Increase in Demand for State and Municipal Government Services
Climate change serves as a threat multiplier, which can increase the need for expenditures to meet existing government service. Examples include capital, equipment, or operating costs for emergency response provision and state sponsored health programs.
Major Level of Consequence
Demand for MassHealth, food security support, and emergency response could be most significantly affected by climate impacts in the Commonwealthmoderate-level-bar.png
Potential for Disproportionality
MassHealth and food security support are generally at the state level and therefore not specific to local incidence, but emergency service support could be disproportionately higher in EJ block groups.
Moderate Adaptation Gap
No identified adaptation actions are underway to address this impact, however the options for direct action are minimal. Adaptation actions directed towards other sectors (e.g., Human and Infrastructure) will also mitigate this impact.
Quick links
- ResilientMass Homepage
- ResilientMass Site Map
- Massachusetts Climate Change Assessment
- Massachusetts Climate Change Assessment – Human Sector
- Massachusetts Climate Change Assessment – Infrastructure Sector
- Massachusetts Climate Change Assessment – Natural Environment Sector
- Massachusetts Climate Change Assessment – Economy Sector
- Massachusetts Climate Change Assessment – Full Statewide Report Volume II
- Massachusetts Climate Change Assessment – Full Statewide Report Volume II, Appendix A
- 2023 ResilientMass Plan
- 2023 ResilientMass Action Tracker