Overview
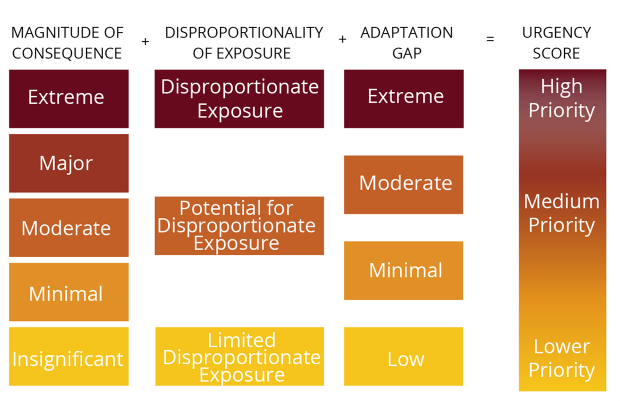
This Climate Assessment considers impacts across five sectors which represent major categories of projected impacts of climate change with common groupings of exposed assets, individuals, or resources, and that generally fall under the responsibility of similar state agencies. The primary objective of the Climate Assessment is to identify urgent climate risk statewide, as well as by each region and sector. Risk rankings were developed through discussions with the project working group and stakeholders, and considered:
-
How big of a climate effect will this have? Quantitative and qualitative indicators of the scale of potential impact, analyzed under the defined future climate scenario.
-
Will populations living in environmental justice areas be disproportionately affected? Demographic analysis of the distribution of impact across populations, particularly the Commonwealth’s identified environmental justice and socially vulnerable groups.
-
Are we currently doing enough to adapt to this impact? Assessment of current and planned adaptation plans and actions, and the potential benefits of additional adaptation action.
Sectors are a helpful organizational structure and allow for the prioritization across impacts with similar types of effects. However, it is important to note that the effects of climate change do not fall neatly within the defined sectors, and there are many interactions between impacts both within and across sectors. To the extent possible, these interactions are noted in the Climate Assessment in order to help draw these connections that may not be seen in the quantitative sectoral analysis.
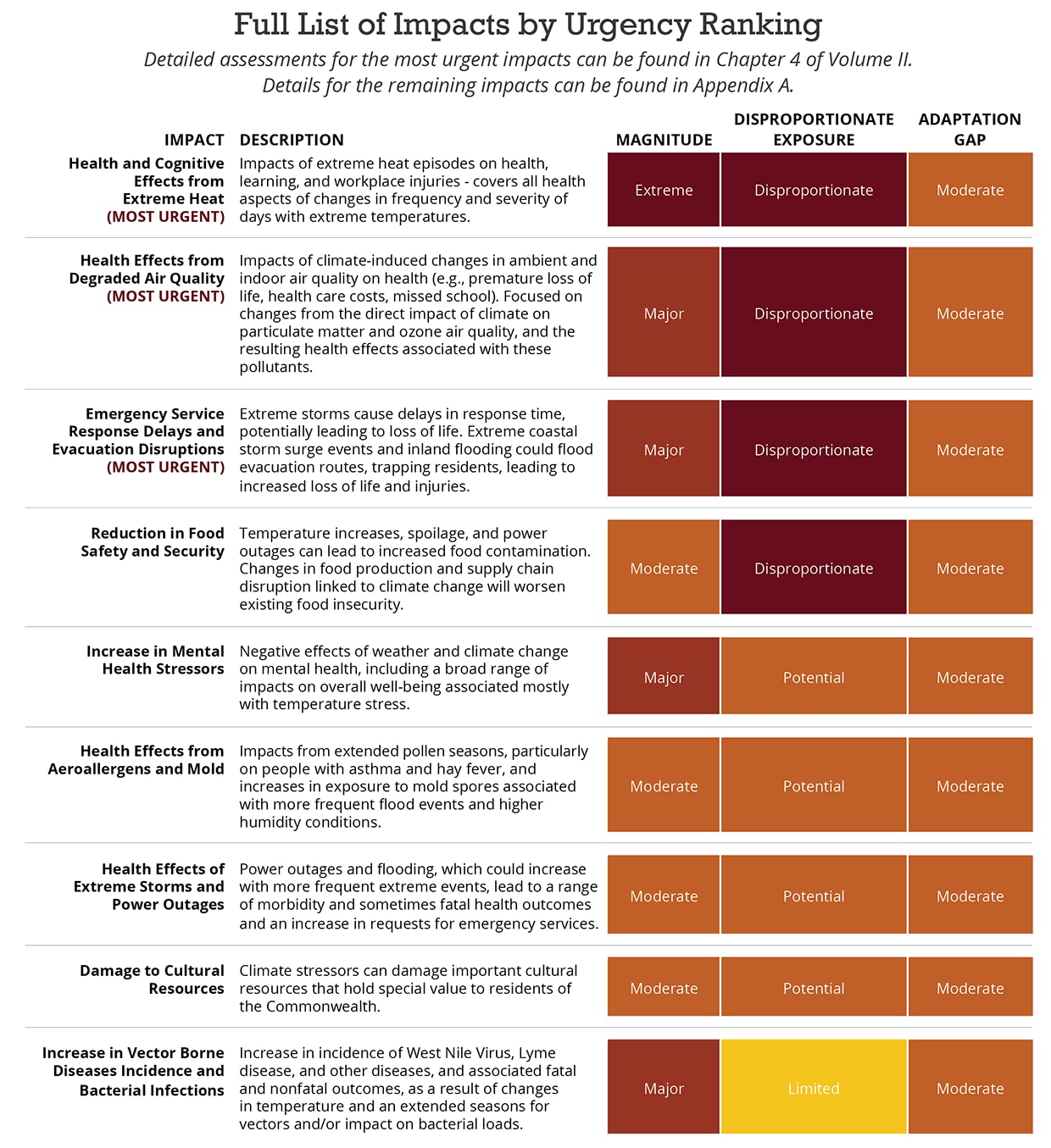
Full List of Impacts in the Human Sector
Nine impacts were evaluated within the Human Sector. Detailed assessments for the most urgent impacts can be found below and in Chapter 4 of Volume II. Details for the remaining impacts can be found in Appendix A.
Most Urgent Impact: Health and Cognitive Effects from Extreme Heat
Impacts of extreme heat episodes on health, learning, and workplace injuries – covers all health aspects of changes in frequency and severity of days with extreme temperatures.
Extreme Level of Consequence
Over 400 additional deaths anticipated by end of century.
Disproportionate Exposure
Linguistically isolated individuals are 28 percent more likely to experience premature mortality as a result of extreme heat.
Moderate Adaptation Gap
Increasing tree canopy cover is a favored solution to combat impacts of extreme heat, especially in urban areas.
Most Urgent Impact: Health Effects from Degraded Air Quality
Impacts of climate-induced changes in ambient and indoor air quality on health (e.g., premature loss of life, health care costs, missed school). Focused on changes from the direct impact of climate on particulate matter and ozone air quality, and the resulting health effects associated with these pollutants.
Major Level of Consequence
Over 100 additional statewide asthma diagnoses annually from air pollution by 2030; over 900 additional asthma diagnoses and 200 deaths by 2090.
Disproportionate Exposure
Minority and language isolated populations are more than 20 percent more likely to live in areas with the highest projected increases in childhood asthma diagnoses.
Moderate Adaptation Gap
Some warning systems and pollution reduction plans in place but technological limitations bound further action.
Most Urgent Impact: Emergency Service Response Delays and Evacuation Disruptions
Extreme storms cause delays in response time, potentially leading to loss of life. Extreme coastal storm surge events and inland flooding could flood evacuation routes, trapping residents, leading to increased loss of life and injuries.
Major Level of Consequence
Effects from flooding roads could increase emergency and law enforcement service response time, particularly in Suffolk and Middlesex counties, leading to indirect effects on mortality and morbidity.
Disproportionate Exposure
All classifications of EJ block groups will experience greater impacts than the rest of the Commonwealth.
Moderate Adaptation Gap
Mitigation measures for road flooding will support evacuation and emergency response teams, but proactive emergency planning and personnel training can be more widely implemented.
Quick links
- ResilientMass Homepage
- ResilientMass Site Map
- Massachusetts Climate Change Assessment
- Massachusetts Climate Change Assessment – Infrastructure Sector
- Massachusetts Climate Change Assessment – Natural Environment Sector
- Massachusetts Climate Change Assessment – Governance Sector
- Massachusetts Climate Change Assessment – Economy Sector
- Massachusetts Climate Change Assessment – Full Statewide Report Volume II
- Massachusetts Climate Change Assessment – Full Statewide Report Volume II, Appendix A
- 2023 ResilientMass Plan
- 2023 ResilientMass Action Tracker