Appearance
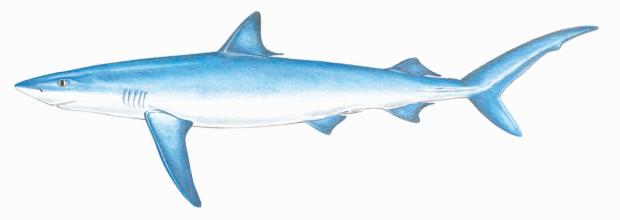
- Blue sharks can get up to 13 feet in length but generally are closer to 10 feet long. They have a deep blue color dorsally, which fades to light blue on the sides and white on the belly. They have slender bodies with large eyes and a cone shaped snout.
Blue shark facts
- Species name: Prionace glauca
- Blue sharks are part of the Requiem shark family.
- They prey on many things including:
- Herring
- Squid
- Cuttlefish
- Smaller sharks
- Sea birds
- Carrion
- Garbage
- Young blue sharks are preyed upon by larger pelagic predators.
- White sharks and shortfin mako sharks are a few of the animals that prey on adult blue sharks.
- Blue sharks birth live young that hatch internally. The gestation period is 9–12 months.
- Average blue shark litters are 25–50 pups, but can get up to 135 pups. The health and size of the female are what determine the litter size.
- Blue shark pups are 16–20 inches long at birth, and are born in central and eastern areas of the North Atlantic ocean.
- Commercial fisheries don't target blue sharks in the United States.
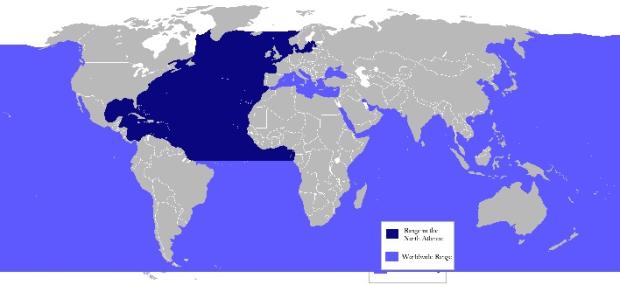
- Blue sharks cover most of the ocean except for the Arctic and southern oceans.
Additional Resources
Angling tips
- Sport fishermen often target blue sharks as they are easy to catch and spend time swimming around boats. You should use a sturdy rod and a traditional larger reel. Herring or bluefish are good bait fish.
- You will have an easier time reeling in a shark if you use a fighting belt and a back harness.
- Blue sharks may roll when hooked, so you should keep the line tense to prevent rolling. However, if a shark rolls, guide it to roll in the opposite direction by pulling the wire up using thick leather gloves.
Contact
Online
DMF Staff Directory
Contact DMF staff
Fax
(508) 990-0449
Address
836 S Rodney French Blvd, New Bedford, MA 02744