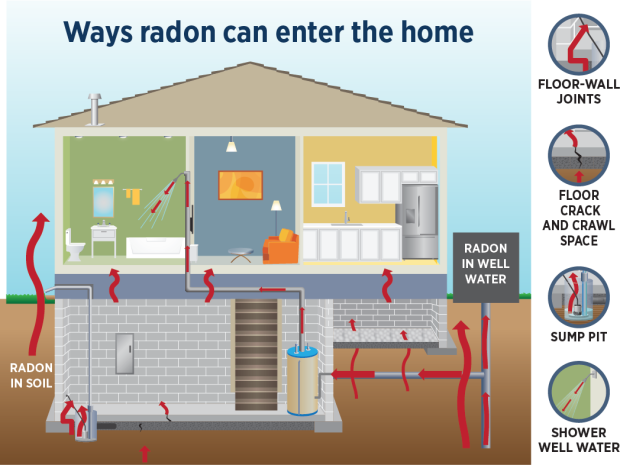
What is radon?
Radon is a radioactive gas that comes naturally from soil and rocks. Radon gas can travel from the ground into a building through cracks and holes in the foundation. Any building, can have high radon levels, no matter the foundation type or whether it has a basement.
What are the dangers of radon?
Radon can build up inside a building and cause lung cancer if you breathe it in over many years. Radon is the #1 cause of lung cancer among people who don’t smoke. Lung cancer risk is much higher for people who are exposed to radon and smoke.
Any radon exposure carries some risk of lung cancer. Lowering the radon level in a building reduces lung cancer risk. You can take the first step to reduce these risks by testing for radon.
Children may face higher risks from radon exposure. They are growing quickly, so they are more sensitive to radiation. Children also spend a lot of time indoors, so they may breathe in more radon than adults. A child’s home is a possible source for radon exposure. Outside of the home, schools and child care programs are additional places where children spend much of their time and may be exposed to radon.
Where is radon a problem?
Any building can have high levels of radon. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency estimates that nearly 1 in 5 schools has at least one frequently occupied ground contact room with radon levels above 4 pCi/L (picocuries per liter of air). Less is known about radon risks in child care programs. No area of Massachusetts is free of radon risk.
How do I know if a building has radon?
You can’t see, taste, or smell radon. The only way to know if a school or child care program has high radon levels is to test for it. Ask the principal or director if they have tested for radon, and ask to see the results.
Visit www.mass.gov/radon for more information on radon testing and mitigation. If you have questions, contact the Massachusetts Radon Hotline at (800) 723-6695.
Additional Resources
-
Open PDF file, 776.7 KB, Radon in Schools and Child Care Programs (English, PDF 776.7 KB)
Contact
Online
Phone
or
The operating hours are Mondays through Fridays from 8:45 a.m.-5 p.m. Please leave a message including your phone number and you will receive a call back.