- Scientific name: Blephilia hirsuta
- Species of Greatest Conservation Need (MA State Wildlife Action Plan)
- Endangered (MA Endangered Species Act)
Description
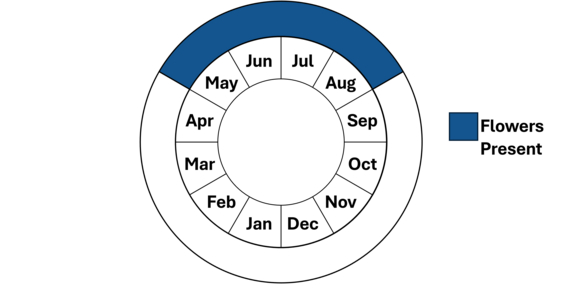
A member of the mint (Lamiaceae or Labiatae) family, hairy wood-mint is an herbaceous perennial, reaching a height of 4-8 dm (12-36 in). Its light-purple flowers and long-stalked, sharply toothed leaves grow from an often unbranched, hairy stem. Hairy wood-mint is typically found in rich, moist forests. Hairy wood-mint has square, erect, and mostly unbranched stems, covered in short hairs, 1-2 mm (0.05-0.1 in) long. The ovate (egg-shaped) leaves are opposite and simple, with serrated (toothed) edges, 4-8 cm (1.5-3 in) long, and have the aroma of peppermint. The leaf bases are rounded and attach to the stem on long petioles. The flowers are nearly white to pale purple, with darker purple spots, and have two lips (formed from five fused petals), 0.75-1.25 cm (0.3-0.5 in) long. Dense clusters or whorls of flowers at the end of the stem are separated from each other by a row of fringed, colored, floral bracts along the stem. Plants bloom from May until August and produce small nutlets. Downy wood-mint (Blephilia ciliata) has blue-purple flowers and also grows to a height of 4-8 dm (12-36 in). Its leaves are short-stalked or stalkless, minimally toothed, and are whitish underneath; stems are downy. Downy wood-mint is also currently listed as Endangered in Massachusetts.
Population status
The MassWildlife’sNatural Heritage & Endangered Species Program (NHESP) database has 13 records, all from Berkshire County. Seven of these records have been observed within the last 25 years.
Distribution and abundance
The documented range of hairy wood-mint extends across North America from Minnesota to Quebec and Vermont. It continues southward through Kansas, Nebraska, and Tennessee.
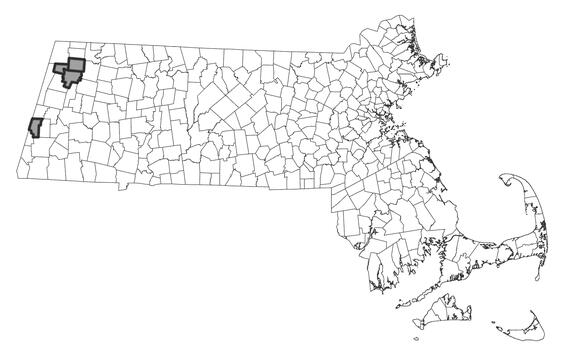
Distribution in Massachusetts
1999-2024
Based on records in the Natural Heritage Database
Habitat
In Massachusetts, hairy wood-mint is commonly found in rich mesic forest. It occurs in the vicinity of small, intermittent streams or river floodplains, and prefers dark, moist soils typical of mature hardwood forests. It is often found with trees such as American beech (Fagus grandifolia), yellow birch (Betula alleghaniensis), red oak (Quercus rubra) and white ash (Fraxinus americana). Associated trees, shrubs, and herbs may include sugar maple (Acer saccharum), basswood (Tilia americana), blue cohosh (Caulophyllum thalictroides), white snakeroot (Eupatorium rugosum), pale touch-me-not or jewelweed (Impatiens pallida), and woodland millet (Milium effusum).
Healthy habitats are vital for supporting native wildlife and plants. Explore habitats and learn about conservation and restoration in Massachusetts.
Threats
Due to its habitat, it is assumed that any disturbance of the particular moisture regime, or the forest habitat, would negatively impact the populations.
Conservation and management
As for many rare species, exact needs for management of hairy wood-mint are not known. The following comments are based primarily on observations of populations in Massachusetts. Hairy wood-mint grows best in rich, mature woodlands, and in areas with moist soils, often in the vicinity of stream and seeps. Mature forest environments should be protected, as should the water quality and levels of small streams and creeks. Trail access to populations should be avoided, and where it occurs, efforts should be made to minimize trampling impacts
Contact
| Date published: | April 8, 2025 |
|---|