- Scientific name: Carex polymorpha
- Species of Greatest Conservation Need (MA State Wildlife Action Plan)
- Endangered (MA Endangered Species Act)
Description
Variable sedge is a vigorous, grass-like herbaceous perennial plant that grows from large rhizomes (rooting underground stems) into dense, spreading colonies. Variable sedge can be easily confused with velvet-fruited sedge (Carex vestita), a species that grows in similar habitats. Whereas velvet-fruited sedge has densely hairy perigynia, those of variable sedge are smooth. The female spikes of variable sedge can be 2.5-5 cm (1-2 in) as opposed to 1.25-2.5 cm ( ½ -1 in), and the stems lack the continuous network of veins which encircle the stems of velvet-fruited sedge. Variable sedge often appears bluish in color, due to small bumps or papillae on its leaf surfaces; velvet-fruited sedge appears uniformly green. Both of these sedges are distinguished from co-occurring woodland sedges by their culms arising singly, rather than in forming even small clumps.
Life cycle and behavior
The stems stand 30-60 cm (12-24 in) tall with long and narrow, 3-5 mm (1/8-1/4 in) wide leaves extending from their base. Each flowering culm has one or two pistillate spikes, which bear 12 to 25 female flowers, and one to three staminate spikes. On the pistillate spikes are bright green, egg-shaped perigynia (seed sacs) with long, slightly curved beaks with obviously oblique tips. Subtending the perigynia are much smaller ovoid scales, dark purplish brown with green centers. In mid-May during the flowering season the plants look bluish green, whereas by September the leaves have turned tawny yellow.
Population status
Variable sedge is listed under the Massachusetts Endangered Species Act as Endangered. All listed species are protected from killing, collecting, possessing, or sale and from activities that would destroy habitat and thus directly or indirectly cause mortality or disrupt critical behaviors. Despite extensive searches throughout its former range, so far it has been rediscovered in only nine of the twelve states where it originally was recorded. Much of its historical habitat may have been destroyed by residential construction and gravel pit operations, so that the total world population of variable sedge is now about 30 current sites. The MassWildlife’s Natural Heritage & Endangered Species Program database has 3 records from 2 counties: Berkshire and Franklin. Only 1 of these records has been observed within the last 25 years.
Distribution and abundance
Variable sedge has a very restricted range within North America, extending from southern Maine to Virginia, and inland to Pennsylvania and West Virginia. Throughout its range, it is considered extremely rare owing to its occurrence as only very localized populations in specialized habitats.
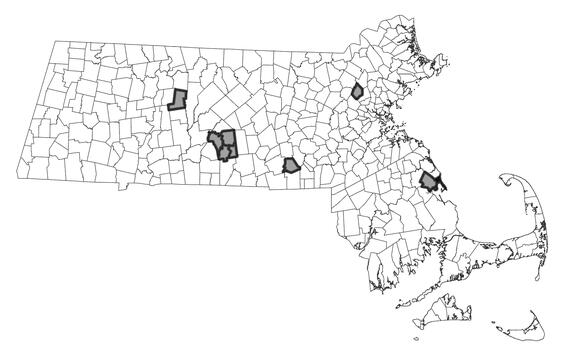
Distribution in Massachusetts
1999-2024
Based on records in the Natural Heritage Database
Habitat
Variable sedge is rarely found fruiting and flowering except when there is abundant light and little competition from other plants. In some states, it grows most vigorously in burned-over areas. Burning seems to stimulate flowering and seed production as well. However, in Massachusetts, variable sedge has not been found in much apparently suitable habitat, indicating that there are other unknown factors influencing its distribution.
Healthy habitats are vital for supporting native wildlife and plants. Explore habitats and learn about conservation and restoration in Massachusetts.
Contact
| Date published: | April 9, 2025 |
|---|