- Scientific name: Oxalis violacea
- Species of Greatest Conservation Need (MA State Wildlife Action Plan)
- Endangered (MA Endangered Species Act)
Description
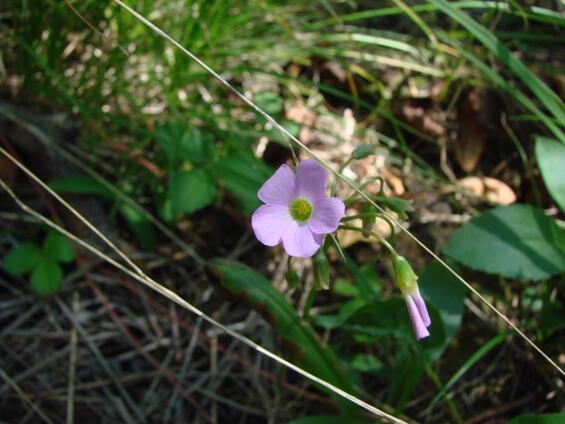

Violet Wood-sorrel (Oxalis violacea)
Violet wood-sorrel (Oxalis violacea) is a low perennial herb of rich, open woodland slopes. A member of the wood-sorrel family (Oxalidaceae), it has heart-shaped, often purple-tinged leaflets and purplish flowers that bloom from late May to early June.
Violet wood-sorrel is stemless, up 25 cm (10 in) in height, with leaves and flower stalks arising from a scaly bulbous base. The leaves are mostly hairless (glabrous) and are compound with three heart-shaped leaflets that are tinged with purple. The flowers are rose-violet, with five petals, and are about 1-2 cm (0.4-0.75 in) in length. They are borne in an umbel atop a stalk 10-20 cm (4-8 in) in height, overtopping the leaves.
Common wood-sorrel (Oxalis montana) resembles violet wood-sorrel in that it is low-growing and stemless, with heart-shaped leaflets. Common wood-sorrel, however, is found in cool, acidic community types, such as spruce-fir forests. It has solitary white flowers that are veined with pink. Other wood-sorrels of Massachusetts (O. corniculata, O. dilenii, and O. stricta) have a stem and yellow flowers.
Life cycle and behavior
This is a perennial species.
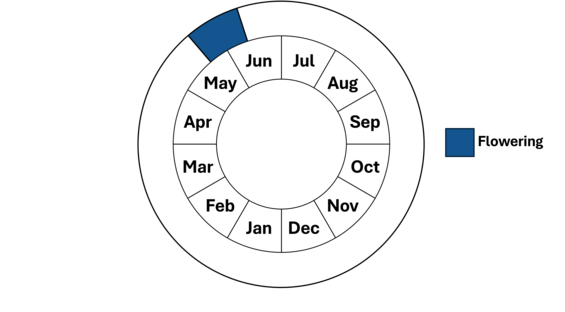
Population status
Violet wood-sorrel is listed under the Massachusetts Endangered Species Act as Endangered. All listed species are legally protected from killing, collection, possession, or sale, and from activities that would destroy habitat and thus directly or indirectly cause mortality or disrupt critical behaviors. The Natural Heritage & Endangered Species Program has 10 records from 5 counties: Bristol, Hampden, Hampshire, Middlesex, and Norfolk. Four of these records have been observed within the last 25 years.
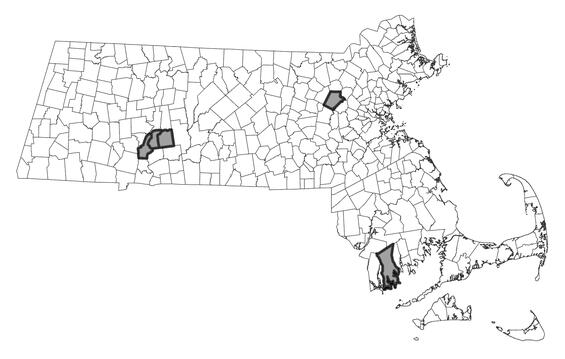
Distribution in Massachusetts. 1999-2024. Based on records in the Natural Heritage Database.
Distribution and abundance
The range of violet wood-sorrel extends from Connecticut and Massachusetts west to North Dakota, and south to New Mexico, Arizona, and the Gulf Coast states. It is also rare in Connecticut, Michigan, New York, and Rhode Island. It is historically known from Vermont.
Habitat
In Massachusetts, violet wood-sorrel inhabits dry or moist rich soils of open deciduous woodlands over circumneutral bedrock. Associated plant species include hickories (Carya spp.), hop hornbeam (Ostrya virginiana), red oak (Quercus rubra), Pennsylvania sedge (Carex pensylvanica), white wood-aster (Eurybia divaricata), wild columbine (Aquilegia canadensis), hepatica (Anemone americana), and sessile-leaved bellwort (Uvularia sessilifolia).
Healthy habitats are vital for supporting native wildlife and plants. Explore habitats and learn about conservation and restoration in Massachusetts.
Threats
Overshading by natural forest succession and invasive plants is a threat to this species.
Conservation
As with many rare species, the exact management needs of violet wood-sorrel are not known. Sites should be monitored for over-shading caused by forest succession, and for invasive plant species. Habitat sites that do not receive enough light can be managed with canopy thinning or prescribed burning. If trampling or erosion are threats in recreational areas, trails can be stabilized or re-routed. To avoid inadvertent harm to rare plants, all active management of rare plant populations (including invasive species removal) should be planned in consultation with the MassWildlife’s Natural Heritage & Endangered Species Program.
Contact
| Date published: | May 12, 2025 |
|---|